Permission Management¶
This feature allow as to manage permissions per view, so we can asociate an specific url name with an specific permission codename and permission category.
Live Demo¶
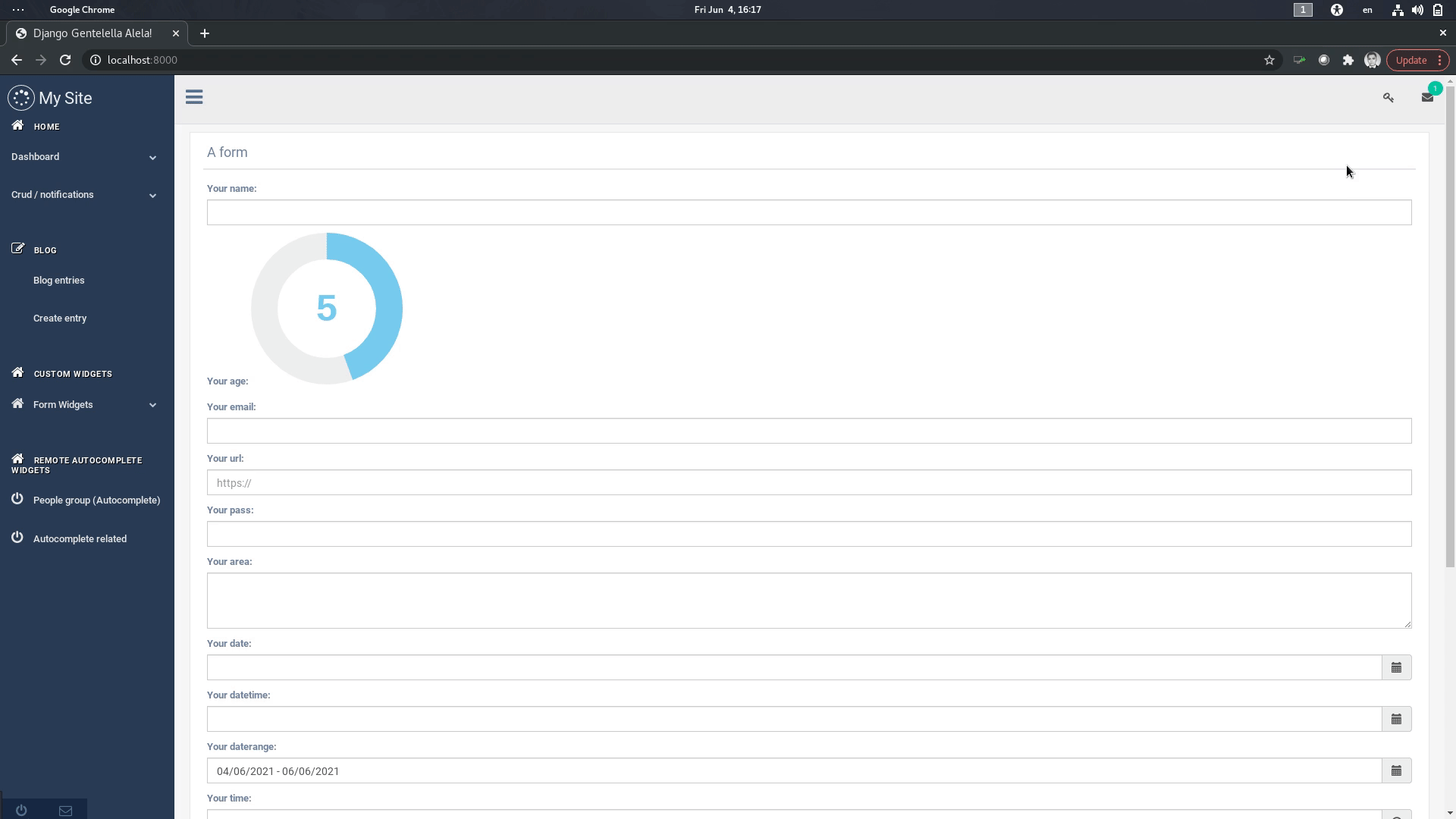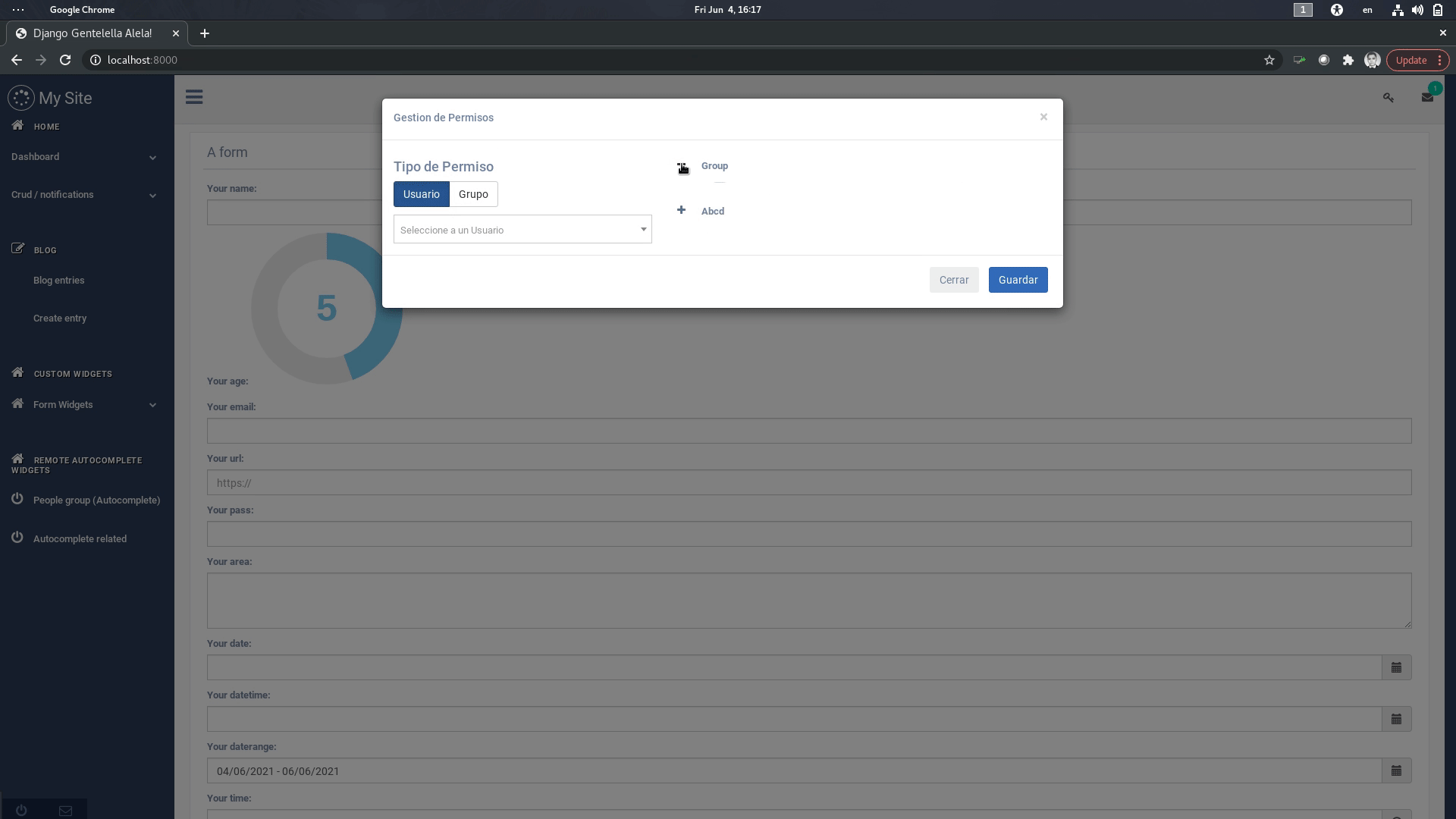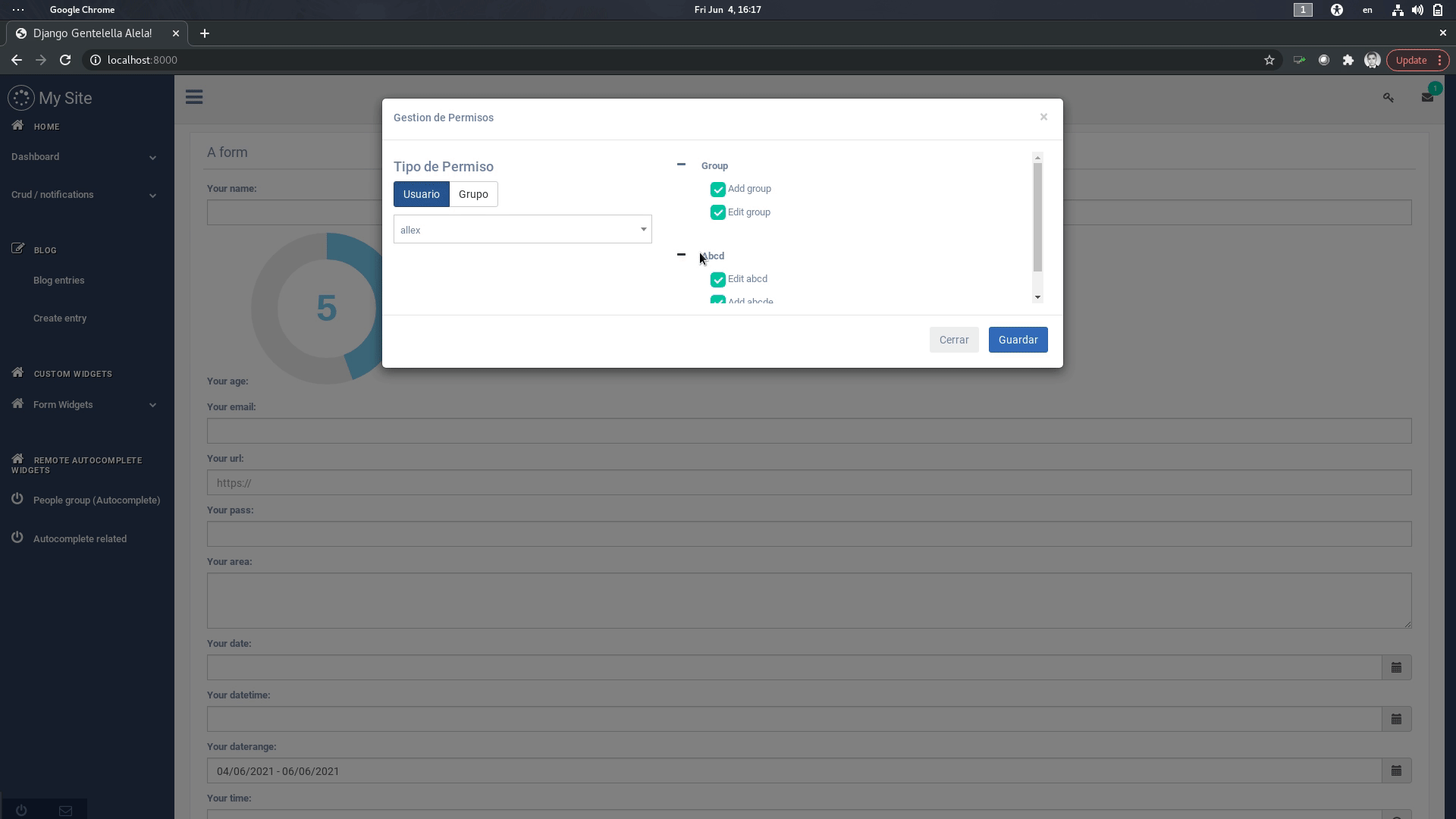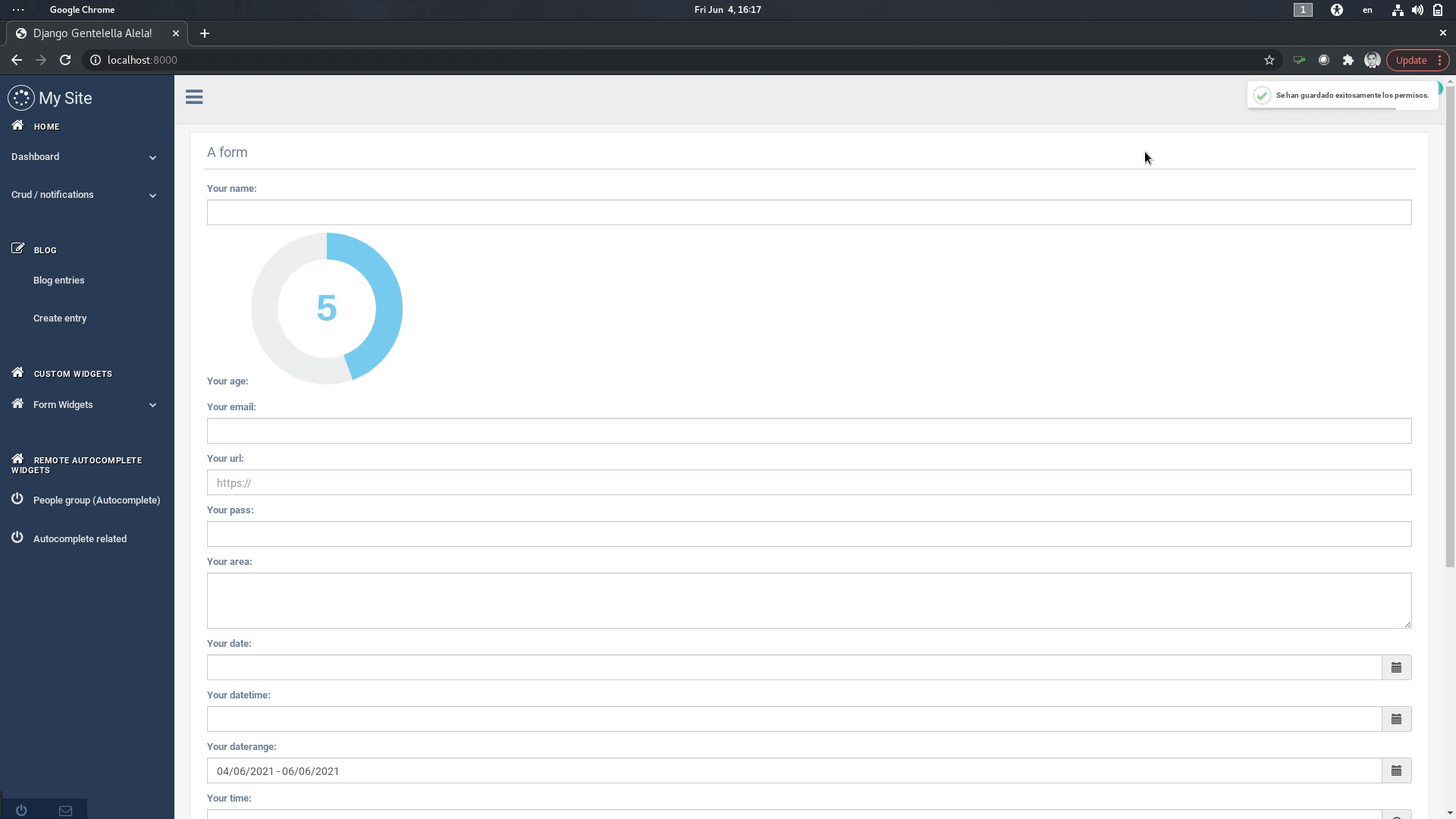
- You can use two main approches to achieve this:
Use get_or_create_permission_context.
Create the permission manually.
Define programatically.¶
You must create a pre_head block as the following example in your template:
{% block pre_head %}
{% get_or_create_permission_context 'pgroup-list' 'demoapp' 'view_peoplegroup' 'List groups' 'Group' %}
{% define_urlname_action 'pgroup-list'%}
{% endblock%}
- The parameters in here are the following:
urlname: Can be a list serparated by commas
appname: This is 78 name of the app asocciated with the permission.
codename: Can be a list of django codenames that are associated with the urlnames.
humanname Is a list names related to the code names this names will be display to the user.
category: Is the name that will join differents permissions together.
Make sure that urlname, codename and humanname has the same number of elements.
It is possible to define also:
{% block pre_head %}
{% get_or_create_permission_context 'pgroup-list,pgroup-edit' 'demoapp' 'view_peoplegroup,change_peoplegroup' 'List groups,Change group' 'Group' %}
{% define_urlname_action 'pgroup-list'%}
{% endblock%}
So we can define a list of permissions in the template tag.
If you want to keep your code clearly:
{% block pre_head %}
{% get_or_create_permission_context 'pgroup-list' 'demoapp' 'view_peoplegroup' 'List groups' 'Group' %}
{% get_or_create_permission_context 'pgroup-edit' 'demoapp' 'change_peoplegroup' 'Change group' 'Group' %}
{% define_urlname_action 'pgroup-list'%}
{% endblock%}
The default behavior of the djgentellela is that if you are superadmin will display de button to manage the permissions similar to the Live Demo.
If you want to change the permissions you can override the following partial gentelella/app/top_navigation.html and also in gentelella/base.html
Define permissions manually¶
To do this you have to go to the admin panel and go to gentellella app:
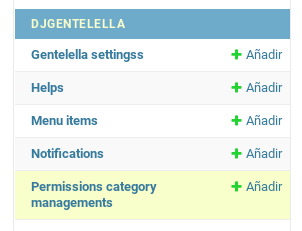
The we can create a new permission as the following example:
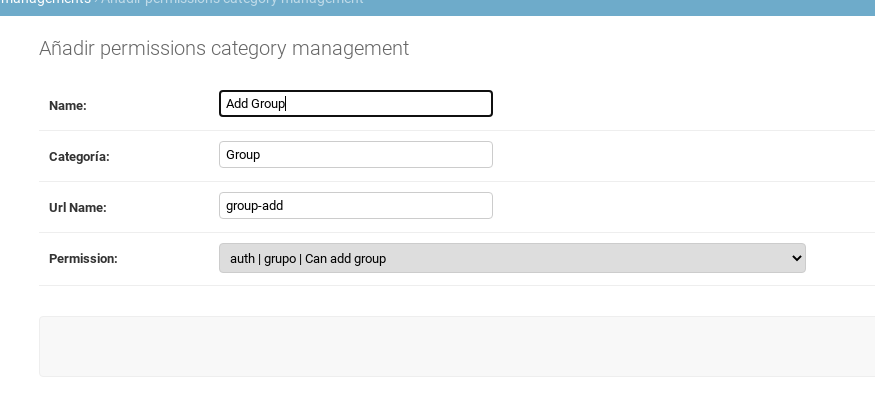
And in your view because you created the permission manually just need to create in your template the following:
{% block pre_head %}
{% define_urlname_action 'group-add' %}
{% endblock%}
It’s really important that you define all the context in the pre_head block otherwise it will not work.
Use different model that User and Group¶
To use different User model you have to add to your settings.py the following:
GT_USER_MODEL = 'demoapp.Employee'
And your custom model need to implement the following function:
class Employee(models.Model):
user = models.ForeignKey(User, on_delete=models.CASCADE)
username = models.CharField(max_length=100)
#username also can be a @property to user.username.
@property
def gt_get_permission(self):
return self.user.user_permissions
def __str__(self):
return self.username
You need a gt_get_permission method that return the relative relation to permissions model. Make sure that you have the username field that can be a CharField or a @property in this way djgentellela will display all the information properly.
To use different Group model you have to add to your settings.py the following:
GT_GROUP_MODEL = 'demoapp.Employee'
And your custom model has to be like the following:
class PermissionsGroup(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=150)
department = models.ForeignKey(Department, on_delete=models.CASCADE)
permission = models.ManyToManyField(PermissionDescription, blank=True)
users = models.ManyToManyField(User, blank=True)
@property
def gt_get_permission(self):
return self.permission
Make suere you have the gt_get_permission and the name field that also of course can be a @property.
Decorators¶
This decorators have 2 optionals parameters
login_url=None Same as login_url of the django decorator login_required
raise_exception=False Same as raise_exception of the django decorator login_required
You can use like:
from djgentelella.decorators.perms import any_permission_required
@any_permission_required(['djgentelella.view_gentelellasettings' 'auth.view_user'],
login_url='/your/url', raise_exception=True
)
def myview(request, *args, **kwargs):
# do your view
any_permission_required¶
Decorator for views that checks whether user has any permission enabled in perms list, redirecting to the log-in page if necessary. If the raise_exception parameter is given the PermissionDenied exception is raised.
from djgentelella.decorators.perms import any_permission_required
@any_permission_required(['djgentelella.view_gentelellasettings' 'auth.view_user'])
def myview(request, *args, **kwargs):
# do your view
all_permission_required¶
Decorator for views that checks whether a user has all permission enabled in perms list, redirecting to the log-in page if necessary. If the raise_exception parameter is given the PermissionDenied exception is raised.
from djgentelella.decorators.perms import all_permission_required
@all_permission_required(['djgentelella.view_gentelellasettings' 'auth.view_user'])
def myview(request, *args, **kwargs):
# do your view